The Easy-K is intended for performing the Kleihauer-Betke test for the detection and quantification of Fetomaternal hemorrhage (FMH). It is a based on the acid elution test developed by Kleihauer, Betke and Braun (1957). The test is based on the differential resistance to acid elution of hemoglobin-F (HbF) and hemoglobin-A (HbA).
Key Benefits
- Detection and quantification of hemoglobin-F containing red blood cells in blood smears
- Ready-to-use reagents
- Microscopic analysis
Features
- Method based on acid elution of hemoglobin-A
- Stains 30 microscopic slides
- Including positive and negative control slides
- Hemalum included to exclude small lymphocytes
- Registered as Medical Device for In Vitro Diagnostic Use (IVD/CE)
Applications
- Determination of Fetomaternal Hemorrhage in:
- Pregnancy with suspected RhD incompatibilities
- Abdominal trauma
Introduction
Detection and quantification of fetal red blood cells (fRBCs) in maternal blood samples is essential for obstetrical management.
Measurement of fRBCs is critical as the extent of fetomaternal hemorrhage (FMH), the transplacental passage of fRBCs into the maternal circulation, has consequences for further treatment of mother and child.
Frequency and size of FMH is directly influenced by complications in abdominal trauma, suspected placental injury or after a caesarean section.
Severe FMH may lead to intra-uterine death. In case of antigen (blood group) incompatibility between mother and child FMH may result in respiratory problems or anemia in newborns.
Detection (and enumeration) of fRBCs is used to calculate the extent of FMH, either in case of trauma with suspected placental injury or in a situation of RhD incompatibility between the fetus and the mother. The amount of fRBCs is a measure to determine the correct dose for the (prophylactic) anti-RhD therapy in order to prevent hemolytic disease in the newborn.
Principle of the Easy-K Kleihauer-Betke test
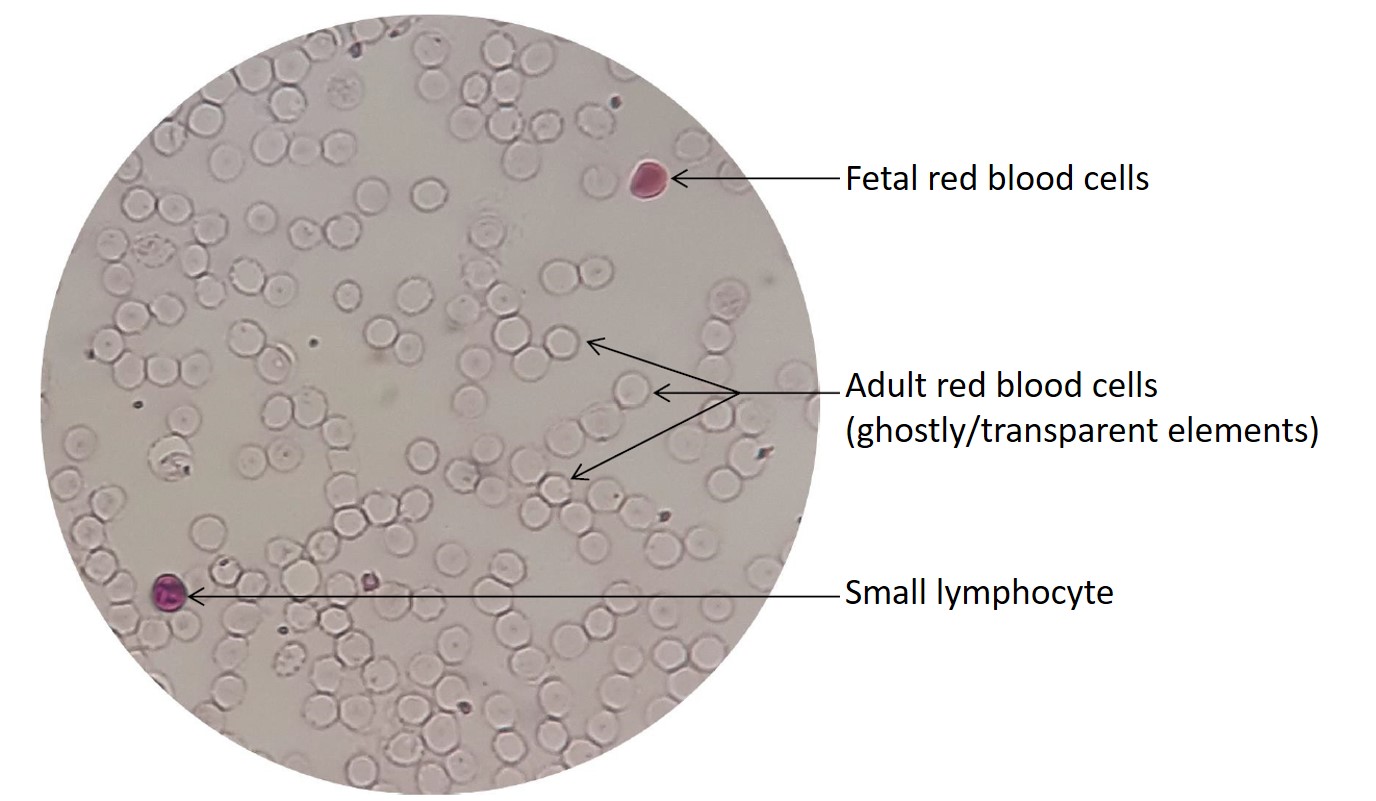
The Easy-K Kleihauer-Betke test distinguishes red blood cells containing hemoglobin-F (HbF) from those that contain hemoglobin-A (HbA). Red blood cells containing HbF are resistant to acid treatment, while cells containing HbA are sensitive for acid treatment. After acid treatment, the HbF remaining in the red blood cells is stained with a pink dye, so the red blood cells containing HbF can be distinguished from the uncoloured HbA containing maternal red blood cells.
Please contact us to receive the instructions for use of the Easy-K
